The force divided by the area is defined to be the pressure. The increase in kinetic energy results in the molecules of gas striking the walls of the container with more force resulting in a greater pressure.

Lecture Presentation Chapter 8 How Water Behaves Bradley
An important relationship derived from the kinetic theory of gases shows that the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules depends only on the temperature.
9how do the molecules of a gas behave. The temperature of a gas is a measure of the mean kinetic energy of the gas. As the gas molecules collide with the walls of a container as shown on the left of the figure the molecules impart momentum to the walls producing a force perpendicular to the wall. 2 the volume of the molecules is negligibly small compared to the volume occupied by the gas.
This number is called a mixing ratio. When you look at really large masses like the Earth and Moon the gravitational pull becomes very impressive. Molecules of a gas remains the same the quantity is constant for a gas regardless of the process through which the gas is taken.
Gas particles are shown to move randomly and rapidly to fill spaces. Molecules are more hyperactive when they reach higher levels of tempature so a gas molecule will behave more wildly than a solid particle at rest. As the gas molecules collide with the walls of a container the molecules impart momentum to the walls producing a force that can be measured.
Molecules are supposed to be points which means no volume without any kind of interactions wi. Gas vibrate and move freely at high speeds. The proportion of CO 2 is currently 0037.
Molecules are more hyperactive when they reach higher levels of tempature so a gas molecule will behave more wildly than a solid particle at rest. 2 the volume of the molecules is negligibly small compared to the volume occupied by the gas. They never exactly do follow the ideal gas equation.
Liquid is shown with no fixed shape and particles moving around. The mixing ratio of a gas is numerically equal to the pressure exerted by the gas denoted for CO 2 as pCO 2. In fact its common for regions of a gas to contain random transient charged regions because of van der Waals forces.
Ions of like charge repel each other while ions of opposite charge attract each other. A gas may contain electrically charged atoms or molecules called ions. Molecules of gas in the atmosphere and nitrogen almost 80.
Gas vs Plasma. Thisforce of attraction has two consequences. The average kinetic energy of the molecules of any gas depends on only the temperature and at a given temperature all gaseous molecules have exactly the same average kinetic energy.
Such a relation for a substance is called its equation of state and is sufficient to describe its gross behaviour. And 3 no forces act on the molecules except during elastic collisions of negligible duration. Answer 1 of 2.
The general gas law can be derived from the kinetic theory of gases and relies on the assumptions that 1 the gas consists of a large number of molecules which are in random motion and obey Newtons laws of motion. We can express that in a more convenient way by saying 370 parts per million or ppm. This theory is based on the following postulates or assumptions.
The gravitational force between the Earth and the molecules of gas in the atmosphere is strong enough to hold the atmosphere close to our surface. These particles move in a straight line until they collide with another particle or the walls of the container. Gases are composed of a large number of particles that behave like hard spherical objects in a state of constant random motion.
Since average kinetic energy is related to the average speed of the molecules E K mu 2 2 where mmass and u is the average speed the temperature of a gas sample must be related to the average speed at which the molecules are moving. The French chemist Joseph Gay-Lussac 1778-1850 discovered the relationship between the pressure of a gas and its absolute temperature. The sum of the forces of all the molecules striking the wall divided by.
Smaller planets that have less mass may not be able to hold an atmosphere. Liquid vibrate move about and slide past each other. The ideal gas law can be derived from the kinetic theory of gases and relies on the assumptions that 1 the gas consists of a large number of molecules which are in random motion and obey Newtons laws of motion.
Gas molecules collide with one another and with the walls of the container but these collisions are perfectly elastic. So if we move the pressure volume and temperature onto the same side of the ideal gas law we get This shows that as long as the number of moles ie. Solid vibrate jiggle but generally do not move from place to place.
Gas molecules are not held rigidly in place as would be a solid or a lattice of ionic bonds instead gas molecules are constantly in motion and each and every different gas exerts a specific pressure. That is they do not change the average kinetic energy of the molecules. 1 gases condense to form liquids at lowtemperatures and 2 the pressure of a real gas is sometimes smaller than expected for anideal gas.
It comes down to the representation of the gas implicit in the ideal gas model. And 3 no forces act on the molecules. Liquids and solids are often referred to as condensed phasesbecause the particles are very close together.
In reality there is a smallforce of attraction between gas molecules that tends to hold the molecules together.

Answered 9 How Will A Gas Velocity Vary If Its Bartleby

Matter Changing States Brainpop Changing States Brainpop What Are The Three Main States Of Matter 2 Compare To Ice How Do Molecules Of Water Behave 3 What Is Matter

Physics And Chemistry 3 Student Book Sample By Grupo Anaya S A Issuu

Lecture Presentation Chapter 2 Particles Of Matter Bradley

Bouncing Off The Walls Elemphys 10 Docx Bouncing Off The Walls Purpose To Control And Observe The Behavior Of Gas Particles Atoms Or Molecules As Course Hero

8 3 1 Grade 5 Standard 1 Unit Test A Matter Multiple Choice 1 A

Chapter 9 How Was The Universe Create How Physics Found God

Gases Notes 12 1 A Physical Properties 1
Soal Toefl Tentang Structure And Written Expression Scholars Official
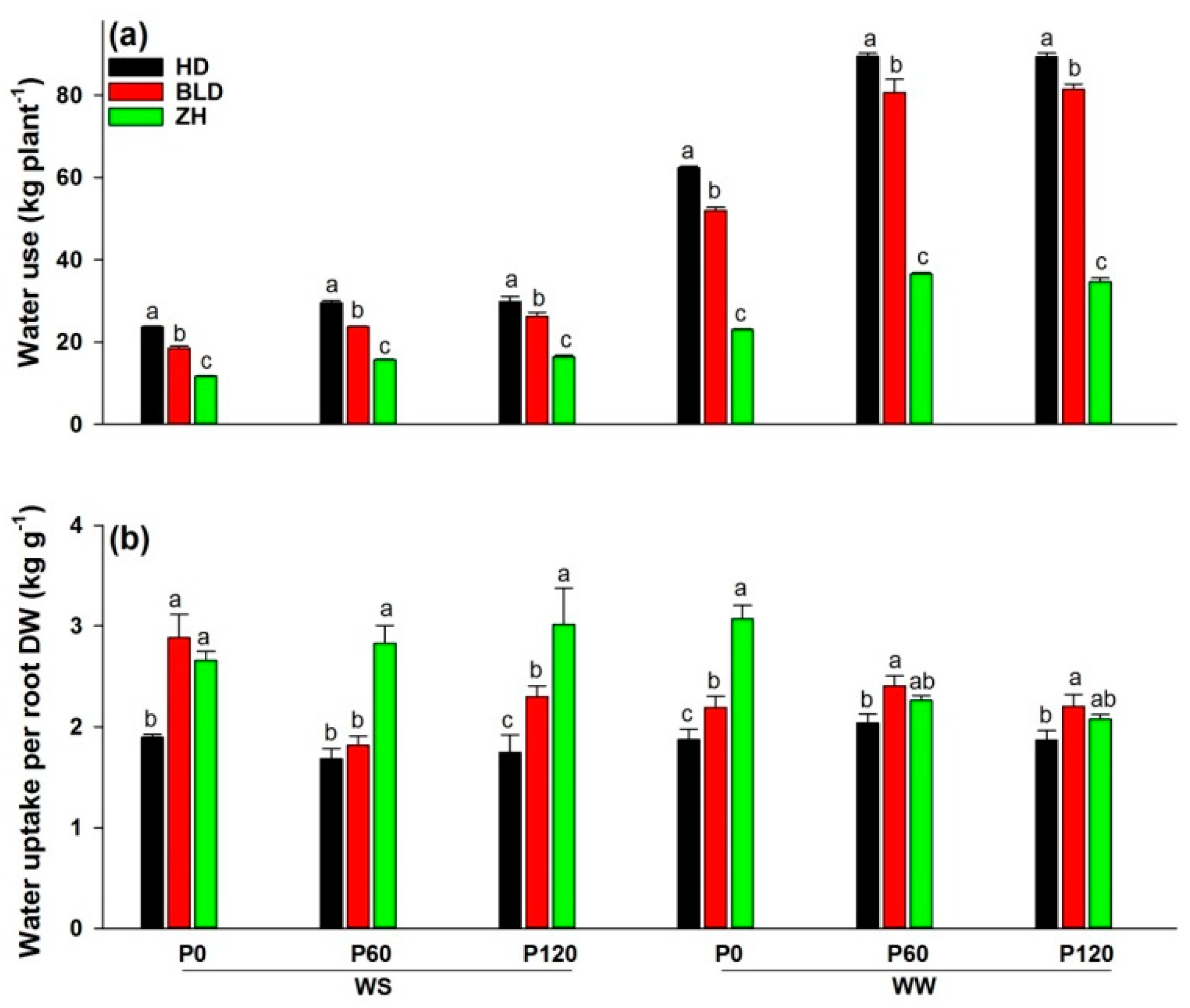
Agriculture Free Full Text Trade Off Between Root Efficiency And Root Size Is Associated With Yield Performance Of Soybean Under Different Water And Phosphorus Levels Html

1 Gases Three States Of Matter 2 3

Organic Chemistry Basic Concepts Teaching In Students Of Large Groups At Higher Education And Web 2 0 Tools

Gases Notes 12 1 A Physical Properties 1
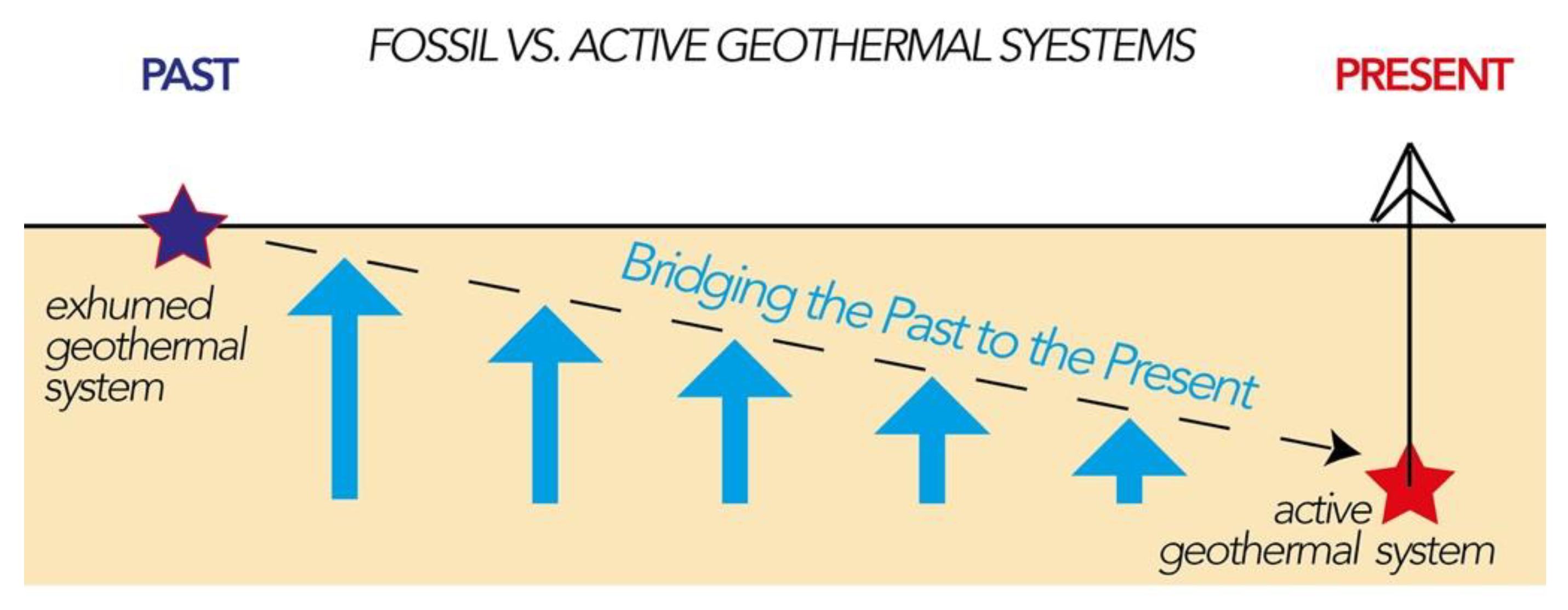
Energies Free Full Text Fossil Vs Active Geothermal Systems A Field And Laboratory Method To Disclose The Relationships Between Geothermal Fluid Flow And Geological Structures At Depth Html

Latihan Soal Ujian Nasional Sma Bahasa Inggris 2019 Dan Pembahasannya

In S 3 O 9 How Many Pi Pi Bonds Are Present

Lecture Presentation Chapter 2 Particles Of Matter Bradley

Latihan Soal Ujian Nasional Sma Bahasa Inggris 2019 Dan Pembahasannya

